Growing More with Data, Precision, and Care!
Precision Agriculture and Smart Farming Technologies: Transforming Modern Farming
In today’s world, agriculture is changing fast. Farmers no longer rely only on traditional methods. They are now embracing ‘precision agriculture and smart farming technologies’ to grow more food with fewer resources. These technologies use tools like GPS (Global Positioning System), sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), drones, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to make farming smarter, faster, and more sustainable. As the global population grows and climate change affects food production, these innovations are becoming essential for feeding the world while protecting the environment.
What Is Precision Agriculture?
Precision agriculture (also called precision farming) means using digital technologies to observe, measure, and respond to field variability in real time so that crops receive exactly what they need; not too much and not too little. It combines data and technology to help farmers make data-driven decisions that save time, money, and natural resources.

Key Technologies in Precision & Smart Farming
Here are the main tools shaping modern agriculture:
GPS & Satellite Technology
GPS helps farmers steer tractors, plan field operations, and map fields with very high accuracy. This ensures planting, spraying, and harvesting are done without overlap, saving fuel and reducing waste.
Sensors and IoT Devices
IoT (Internet of Things) sensors placed in fields collect real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels. This information helps manage irrigation, detect problems early, and avoid wasteful practices.
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
AI analyzes large amounts of data gathered from sensors and drones to predict issues like pest attacks, water stress, and crop diseases. AI helps farmers take action before problems get worse.
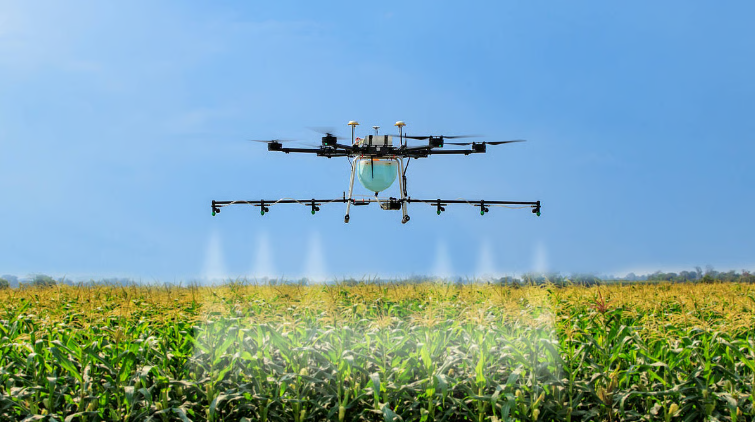
Drones (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles)
Drones fly over fields capturing high-resolution images that show crop health, water needs, and pest infestations. This helps farmers monitor large areas quickly and accurately. Farmers can even use drones for targeted spraying of fertilizers and pesticides.
Autonomous Machinery & Robotics
Smart tractors and robotic harvesters can work with precision using GPS and sensor data. They reduce labor needs, operate consistently, and improve efficiency.
How These Technologies Are Helping Farmers Today
Improved Crop Monitoring
Tools like drones and sensors allow farmers to see what’s happening in the field every day without walking long distances. This leads to early detection of crop stress, diseases, and nutrient deficiencies.
Efficient Irrigation Management
Smart irrigation systems use soil moisture data to water crops only where and when needed. This can save up to 25–35% of water while maintaining plant health.
Higher Yields & Resource Use
Precision farming helps increase crop productivity by giving plants the right amount of water and nutrients. It also reduces waste, meaning less fertilizer and pesticide use overall.
Environmental Sustainability
By using inputs more accurately, precision agriculture reduces pollution, conserves water, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. This supports long-term environmental health.
Current Developments in Precision Agriculture
- Governments are investing in AI and smart agriculture programs — for example, policies offering funds and training for farmers to adopt AI and smart tools.
- Universities and research centres are collaborating on precision farming research, combining AI, IoT, drones, and robotics for better field solutions.
- Advanced drones with multispectral and hyperspectral cameras can detect issues in crops many days before visible signs appear, helping prevent crop loss.
Why Precision Agriculture Matters Now
Precision and smart farming technologies are not just trends. They are solutions for global challenges such as:
- Population growth requiring more food production.
- Climate change causing unpredictable weather.
- Water scarcity and soil degradation.
- Need for sustainable farming with lower environmental impact.
By using technology, farmers can adapt to these challenges and continue to grow safe, high-quality food for the world.
Conclusion: The Future of Smart Farming
Precision agriculture and smart farming technologies are transforming the future of farming. With tools like GPS, IoT sensors, AI, and drones, farmers can monitor crop health, optimize resource use, and make informed decisions faster than ever before. These innovations help increase crop yields, reduce costs, protect the environment, and build climate-resilient farming systems. As technology continues to advance, precision agriculture will play a vital role in ensuring sustainable food production for future generations.